

 Source: Latvijas valsts meži
Source: Latvijas valsts mežiArea of Latvian forests in hectares
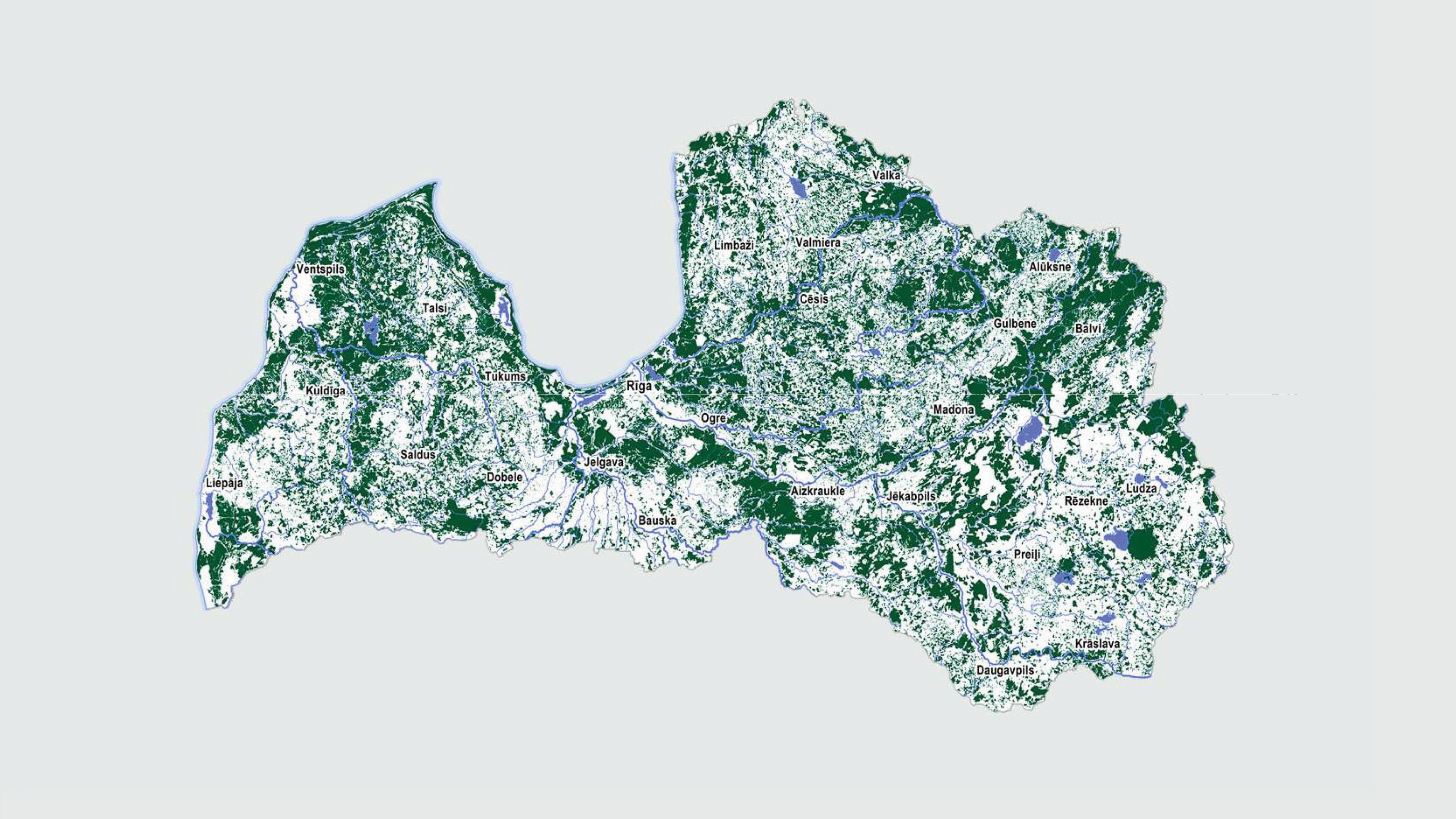
The territory of Latvia is covered by forest
1. Territories
2. Forestry
The forest sector in Latvia is under the supervision of the Ministry of Agriculture. It works with stakeholders to draft forest policies, development strategies for the sector, as well as regulations on forest management, the use of forest resources, environment protection and hunting.
www.zm.gov.lv
The State Forest Service, under the Ministry of Agriculture, is the responsible agency for supervising how the provisions of the laws and regulations are observed in forest management irrespective of the ownership type.
www.zm.gov.lv/valsts-meza-dienests
State-owned forests are managed by Stock Company "Latvian State Forests", which was established in 1999. It implements the state's interests in terms of preserving and increasing the value of the forest and enhancing the contributions of the forest to the national economy.
www.lvm.lv
The interests of private forest owners are represented by the Latvian Forest Owners' Association.
www.mezaipasnieki.lv
3. Contribution to the economy
4. Contribution to the energy sector
5. Timber industry
Latvian timber industry associations
- Association "Latvijas Mēbeles" (Latvian Furniture)
- Latvian Timber Producers and Exporters Association
- Latvian Association of Wood Processing Companies and Exporters
- Association "Latvijas Koks"
- Latvian Union of Timber Harvesting Companies
- Latvian Association of Independent Timber Harvesting Companies
- Latvian Biomass Association LATbio
- Latvian Wood Construction Cluster









6. Foreign trade
7. Forest sector and society
8. Education
Faculty of Forest and Environmental Sciences
121 new forest sector specialists graduated from the LBTU Faculty of Forest and Environmental Sciences in 2025.In Bachelor's degree programs:
43 Forest Engineering
14 Wood Processing
In Master's degree programs:
5 Wood Materials and Technology
19 Labour Safety
In Doctor's degree programs:
2 Wood Materials and Technology
Vocational education institutions offering forest sector-related specialties
9. Science
Latvian State Forest Research Institute "Silava"
www.silava.lv- Forest economics
- Forest remote sensing and GIS
- Unmanned aerial vehicle technologies in forestry
- Genetic analysis method competences
- Forest ecosystem services assessment methodology
- Plant physiology
- Forest wood resource forecasting and modeling
- Forest (forestry) and climate interaction
- National Forest Monitoring Program
- Genetic Resources Centre
- LULUCF sector GHG emissions and CO2 sequestration accounting and forecasts
- Evaluation of suitability of reproductive material produced in other countries for use in Latvia
Latvia University of Life Sciences and Technologies
www.lbtu.lv WOOD UTILIZATION RESEARCH DIRECTION- Development of fire protection agent with sustainable and low environmental impact
- Industrially manufactured facades (shield systems)
- Development of wood composite materials and their application possibilities
- Technical-economic research of wood bonding technologies
- Research of wood cutting processes
- Research of wood hydrothermal treatment processes
- Furniture construction and conformity assessment
- Wood properties prediction
- Use of lignocellulose-based materials in insulation material production
- Rare and protected species, their changes, adaptation and risk factors in the context of climate change
- Anthropogenic impact on forest biodiversity and green infrastructure planning solutions
- Innovative solutions for increasing forest ecosystem diversity and promoting resilience
- Impact of economic activities on forest bird species
- Opportunities to provide microhabitats and other biodiversity elements
- Social research on forest and human interaction and its use in forest policy decisions
- Impact of conifer and deciduous tree mixtures on carbon stock and GHG dynamics
- Effectiveness of climate change mitigation in continuous cover forestry
- Afforestation solutions with the greatest climate change mitigation effect
Forest Research Station
www.agenturamps.lvLatvian State Institute of Wood Chemistry (WCI)
www.kki.lv- Wood Degradation and Protection Laboratory
- Biorefining Laboratory
- Cellulose Laboratory
- Lignin Chemistry Laboratory
- Polymer Laboratory
- Bioengineering Laboratory
Forest and Wood Products Research and Development Institute
www.e-koks.lv Fields of activity:- Materials and technologies
- Fire safety
- Energy
- Economics
University of Latvia
www.lu.lv- Innovative information technologies
- Climate change and sustainable use of natural resources
- Ecology and biodiversity
- Public health, quality of life, and national sustainability
- Human and technologies, quality of education
- Faculty of Exact Sciences and Technologies (EZTF)
- Faculty of Medicine and Life Sciences (MDZF) – Institute of Biology
Vidzeme University of Applied Sciences
www.va.lvRiga Technical University
www.rtu.lvDaugavpils University
www.du.lvThe forest research station, which is an agency founded by Latvian state forest research institute "Silava" and Latvia University of Life Sciences and Technologies forest faculty, conducts scholarly research in the area of forest management, ensuring long-term and uninterrupted research in this area.
www.agenturamps.lv